Article Contents
Introduction
Medicare and Medicaid benefits are government-backed healthcare programs. They serve different groups of people and have different eligibility requirements. However, it is possible for some people to qualify for both programs.
It’s important to understand the differences between Medicare and Medicaid benefits. Each one works so that if you’re eligible for either or both, you can receive all the benefits offered to you.
What is Medicare?
Medicare is a federal program that offers healthcare coverage, but they come in “parts.” One is, Part A. which covers hospital stays and insurance. While Part B, covers outpatient care.
When people refer to Medicare, they usually mean Original Medicare – which consists Part A and Part B.
Medicare Advantage
Medicare Advantage, also known as Medicare Part C, covers everything in Original Medicare. It helps bundle Part A and Part B into a single plan. These plans usually include additional benefits that Original Medicare doesn’t offer. It is provided by private insurers who follow guidelines set by the government.
People at least 65 years of age who are U.S. citizens or permanent residents are eligible for Medicare. Most people who qualify for social security also qualify for Medicare.
People younger than 65 with certain disabilities also qualify. Those with kidney issues also qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid benefits.
What Does Medicare Cover?
Original Medicare covers hospital stays, skilled nursing, home health care, and hospice care. It also covers doctor’s visits, mental health services, therapy, and other outpatient services.
The original Medicare does not cover prescription drugs, eyeglasses, hearing aids, or dental treatments. Those who choose the Original Medicare can purchase prescription drug coverage.
Medicare Advantage covers everything included in Original Medicare. Also, these plans usually come with prescription drug coverage which is a great way to save money. It frequently offers dental and vision coverage, hearing aids, and fitness benefits. These coverages vary by Medicare and Medicaid benefits plan.
Medicare comes with a Cost
- Part A– pays for hospital services, is free if you or your spouse paid Medicare payroll taxes for at least 10 years. (Individuals who are not eligible for free Part A can pay few hundred dollars per month.)
- Part B- covers doctor visits and outpatient services. It comes with a monthly price tag—the standard premium in 2020 was $144.60 per month and rose to $148.50 in 2021.
- Part D– covers prescription drug costs. It also has a monthly charge that varies depending on which plan you choose.
The average Part D basic premium in 2022 is about $33 a month, roughly the same as last year. Besides premium costs, you’ll also have co-payments, deductibles, and other out-of-pocket costs.
Which MediGap Option Is Right For You?
Beneficiaries of traditional Medicare will sign up for a Medigap supplemental insurance plan. Private insurance companies offer these to help cover deductibles, co-payments, and other gaps.
Your Medigap plan can be changed at any time. However, you’re likely to be charged more or denied coverage if it’s over six months since the initial registration for Part B.
Medigap policies go from A and N. Each policy with the same letter must offer basic benefits. Usually, the only difference between policies with the same characters is cost.
Plan F is the most popular policy for its comprehensive coverage. However, after 2020, Plan F (and Plan C) will no longer be available to new participants. The closest alternative to Plan F is Plan G. It pays for everything that Plan F did except the Medicare Part B deductible. Ones who enrolled in Medicare before 2020 can enroll in Plans F and C still.
What Is Medicare Advantage?
You can choose to sign up for traditional Medicare: Parts A, B, and D, and a supplemental Medigap policy. Alternatively, you can take another route and sign up for Medicare Advantage.
- This will provide medical and prescription drug coverage through a private insurance company. Medicare Advantage, also known as Part C, has a monthly fee. The premium for Part B depends on the plan you choose.
- Medicare Advantage is a great option for those who don’t want to sign up with Medicare Part D or buy Medigap coverage. Like traditional Medicare, you’ll also be subject to co-payments, deductibles, and other costs. Advantage plans often charge lower premiums than Medigap plans.
- But do keep in mind, they have higher cost-sharing. With Medicare Advantage, you may have fewer choices of providers to choose from compared to traditional Medicare. Recent research has found that sicker enrollees dump Medicare Advantage for Original Medicare.
What Medicare Does Not Cover?
While Medicare covers your health care, it generally does not cover long-term care. This is an important distinction. Under certain conditions, particularly after a hospitalization, to treat an acute-care episode. Medicare will pay for medically necessary skilled nursing facilities or home health care.
However, Medicare usually does not cover the cost of “custodial care”. It’s the type of care that helps with activities of daily living such as changing clothes, eating, and bathing. If you meet the income and asset requirements, you will have to rely on your savings, long-term-care insurance, or Medicaid to cover those costs. Traditional Medicare doesn’t cover routine dental care or eye exams. It also doesn’t provide coverage for some items such as dentures, hearing aids and such!
What Is Medicaid?
Medicaid is a joint program between the government and states. It ensures people with low incomes have healthcare access.
Medicaid provides health coverage for the following:
- families and children,
- pregnant people,
- the elderly,
- people with disabilities, and
- some people with low incomes.
In the 39 states (including Washington, D.C.), most adults under 65 who have an income lower than 138% of the federal poverty level are eligible. In 2021, that amount is $12,880 for an individual and $21,960 for a family of three.
As a result of those 12 states choosing not to expand Medicaid, there is limited coverage for nonelderly adults. This is especially true for people who have a child, pregnant women, or people who have a disability.
What Does Medicaid Cover?
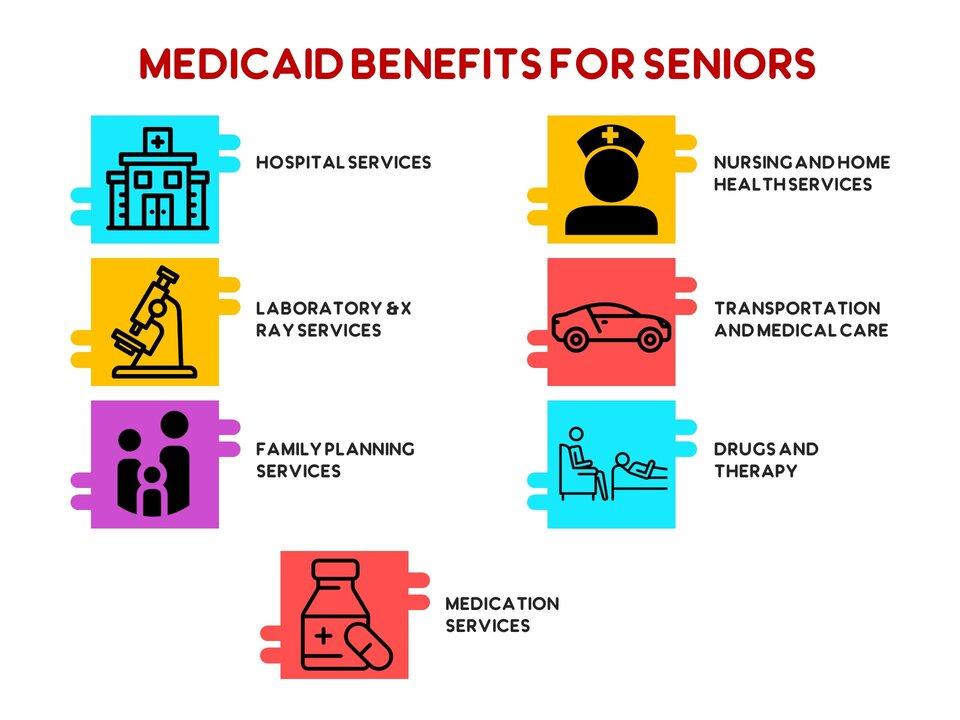
According to federal guidelines, some Medicaid benefits (in all plans) have to be offered across all states, that include:
- Coverage for hospital stays
- Outpatient hospital services
- Laboratory and X-ray services
- Family planning services
- Nursing facility services
- Home health services
- Doctor visits
- Transportation to medical care
Some of the optional benefits states can choose to offer include:
- Prescription drugs
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech, hearing, and language disorder services
- Respiratory care services
- Optometry services
- Dental services
Medicare vs Medicaid- What Is The Better Option For Seniors?
There can be some confusion around Medicare and Medicaid, partly because of the similar names.
But both are very different healthcare programs provided by the government. So what is the difference between Medicare and Medicaid? See in the table below:
|
Medicare |
Medicaid |
|
Focuses on older adults and disabled individuals regardless of the income |
Focuses on low income individuals and families irrespective of age |
|
Covers short-term care services |
Covers long-term care services |
|
Charges premiums or deductibles |
Generally free |
|
Funded and managed by Federal Government |
Funded managed by Federal & State Government |
Medicare focuses on adults aged 65 and older, and Medicaid focuses on low-income individuals and families. The benefits, costs, and eligibility requirements are different for each program. Neither program has automatic enrollment, so it’s important to understand what each one offers.
Being aware of which program to apply for, helps maximize older adults’ healthcare benefits. The vastly different eligibility criteria is the first and biggest difference between Medicare and Medicaid.
People who qualify for Medicaid might not be able to get Medicare and vice-versa, because of their very different eligibility criteria. The second key differentiator is Medicaid covers long-term care services, unlike Medicare. Medicaid is the largest single source for funding long-term care in America.
Medicaid can cover the cost of the following services if they are considered medically essential:
- nursing homes,
- assisted living communities, and
- other long-term care alternatives.
Generally, Medicare only covers short-term stays in skilled nursing facilities after a hospitalization.
Consider Dual Eligibility
Dual eligibility means when an individual qualifies for both Medicare and Medicaid. In such cases, they might hold an original Medicare (parts A and B) or an Advantage plan (Part C). Your prescription drugs under Part D will also be covered by Medicare.
Medicaid may also offer coverage for services that Medicare doesn’t. So, having both will probably cover most of your healthcare costs. Medicare and Medicaid are two U.S. government programs. Both are designed to help different populations get access to healthcare.
Medicare covers citizens aged 65 and over and those with certain chronic conditions or disabilities. In contrast, Medicaid eligibility is mainly based on income level and need. Beneficiaries with Medicare and Medicaid are dual-eligible. They account for about 20 percent of Medicare beneficiaries (12.1 million people). Dual eligibility is categorized based on what percentage of the Medicaid benefits they receive.
Which One Is The Better Option?
Full-benefit dual-eligible have comprehensive Medicaid coverage. While partial benefit, you may get help with premiums and cost-sharing through a Medicare Savings Program (MSP). (Some beneficiaries have Medicare, Medicaid, and an MSP.)
Medicare is a federal program, meaning that the government regulates eligibility across all states. But the eligibility rules for Medicaid and MSPs (within federal guidelines) vary by state. Income limits can vary quite widely for these programs.
With dual-eligible Medicare and Medicaid benefits, Medicare pays first, and Medicaid pays last. However, this does not apply to things that Medicare does not cover, such as long-term care. If Medicaid covers long-term care, Medicare will continue to be the primary payer of all services covered by Medicare. This includes services like skilled nursing care or physical therapy.
Although it is not that common, Medicare pays for a dual eligible individual who has additional coverage (e.g. Medigap plan). Medigap pays second, and Medicaid is the last one to pay for the claims (for costs covered by all three).
What is the Income Range for Beneficiaries who are Dual-Eligible?
Generally, beneficiaries earning less than 135 percent of the federal poverty level are eligible for the MSP. If they have limited savings (although some states don’t require beneficiaries to have low assets). That’d be $17,226 annually for single beneficiaries and $23,274 for couples. The state provides full benefits to those who have ever less incomes and assets (but the amounts vary from state to state).
Many seniors who live in nursing homes are dual-eligible. For Medicare benefits, they qualify based on their age while for Medicaid their financial circumstances determine eligibility. It is also common for Medicare beneficiaries under 65 to receive Medicaid benefits.
Can I select an Insurance Plan for my Medicare and Medicaid Benefits?
If you are dual-eligible, you can enroll in a dual-eligible special needs plan (D-SNP) that covers both Medicare and Medicaid benefits. These plans may also pay for expenses that Medicare and Medicaid don’t cover individually. They include over-the-counter items, hearing aids, and vision or dental care.
Dual eligible beneficiaries can change between original Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans. Alternatively, they switch Part D plans each quarter.
Medicare- what is is, whom it covers
Medicaid- what it means, whom it covers, the difference between these two insurance plans, what seniors need to know about these programs, and how to benefit from them.
Blog keynote
Conclusion
Medicare and Medicaid benefits are a difficult and complex topic. Most people don’t really understand what the difference between these two plans is. You can learn more about it by learning more about their prospective plans.
Healthcare insurance is important and it’s necessary to understand the difference between these two plans. So, make sure that you understand before you make the decision. BoomersHub is here to guide you with any confusion you may have.
Interested to learn more about Medicare benefits? You may like also:


1 comment
Great. Thank you
Comments are closed.